Poverty in India
POVERTY IN INDIA: FACTS, CAUSES, EFFECTS, SOLUTIONS
INTRODUCTION
Food, water, and shelter have been defined as the basic needs of man. The modern list adds health, education, and sanitation to the 3 stated earlier. The inability to fulfil these basic requirements is termed as poverty. Poverty in India follows both income-based and consumption-based statistics.
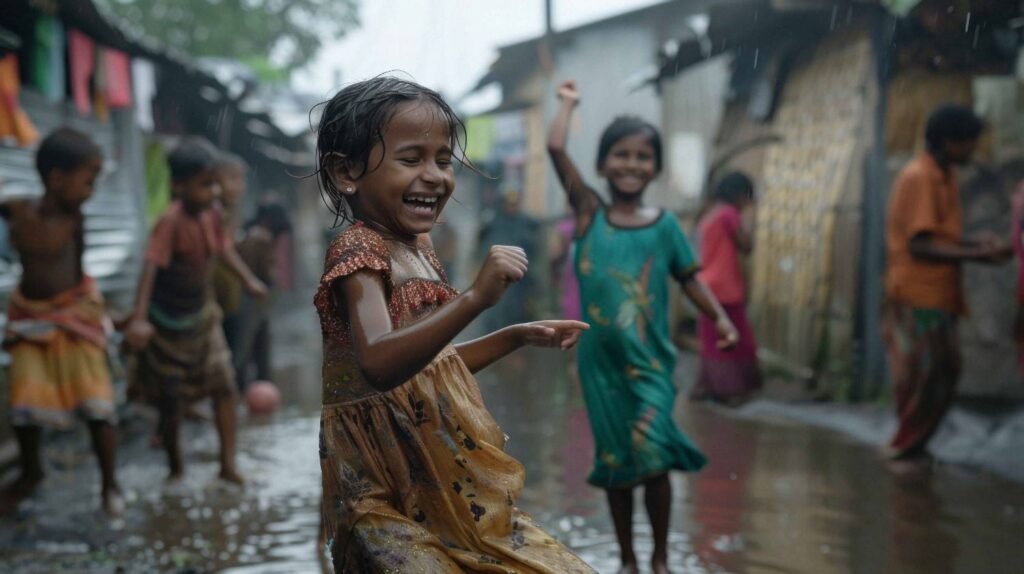

Absolute poverty and Relative poverty are the types of poverty used for defining poverty. India, which is known as one of the fastest growing economies of the world, still struggles to eradicate poverty. The fact that the rich are getting richer and the poor are getting poorer is alarming. Let us learn about poverty in India, it’s causes, effects, and solutions.
QUOTE
“Overcoming poverty is not a gesture of charity, it is an act of justice.” – Nelson Mandela
“Poverty is the worst form of violence.” – Mahatma Gandhi
“Poverty often deprives a man of all spirit and virtue, it is hard for an empty bag to stand upright.” – Benjamin Franklin
STATISTICS – What Numbers have to Say?
📉 Decline in Multidimensional Poverty
According to a 2024 NITI Aayog report, India’s multidimensional poverty rate decreased from 29.17% in 2013-14 to 11.28% in 2022-23. This translates to approximately 24.82 crore (248.2 million) individuals moving out of poverty during this period. The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) assesses deprivations across health, education, and standard of living indicators.
📊 Monetary Poverty Rates Reach Historic Lows
The State Bank of India’s 2025 report indicates that India’s overall poverty rate fell below 5% in 2024. Rural poverty declined to 4.86%, while urban poverty dropped to 4.09%. These figures reflect a significant improvement from previous years, highlighting the effectiveness of targeted government initiatives and economic growth.
🌍 Reduction in Extreme Poverty
Data from the World Poverty Clock reveals that the proportion of Indians living in extreme poverty (earning less than $2.15 per day) decreased to 2.4% in 2024, down from 3.3% in 2022. This decline signifies substantial progress in alleviating severe economic hardship.
🏆 State-Level Achievements
Several states have demonstrated notable reductions in poverty:
-
Uttar Pradesh: Approximately 5.94 crore people exited multidimensional poverty.
-
Bihar: Around 3.77 crore individuals improved their living conditions.
-
Madhya Pradesh: About 2.30 crore citizens moved out of poverty.
-
Rajasthan: Nearly 1.87 crore people experienced improved socio-economic status.
These advancements are attributed to enhanced access to nutrition, education, sanitation, and clean cooking fuel.
🛠️ Government Initiatives Driving Change
Key programs have played a pivotal role in poverty reduction:
-
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY): Provides free food grains to over 81 crore beneficiaries, ensuring food security for vulnerable populations.
-
LIFE Mission in Kerala: Completed 4.5 lakh houses and uplifted nearly 60,000 extremely poor families, contributing to the state’s low multidimensional poverty index of 0.48%.
🚨 Ongoing Challenges
Despite significant progress, certain areas require continued attention:
-
Homelessness in Urban Areas: Delhi faces a homelessness crisis, with over 300,000 individuals lacking stable shelter. Existing infrastructure meets only 10% of the demand, highlighting the need for comprehensive urban housing solutions.
-
Economic Hardship Among Tribals: In Jharkhand, over 46% of indigenous communities live below the poverty line, facing challenges such as limited access to social protection schemes and land conflicts.
DESCRIPTION – Let’s take a Deep Dive
CAUSES OF POVERTY IN INDIA
- The exponentially growing population stands the main cause behind most of the major problems faced by the country. This increasing population has further led to unemployment and lower per capita income.
- Illiteracy makes people take up labor jobs or jobs based on daily wages. Unskilled workers get paid very low compared to the amount of physical work done for the whole day.
- The ever-increasing price of basic commodities makes it difficult for people below the poverty line to afford survival.
- The Indian economy is underdeveloped due to the low rate of growth. The net national income is low compared to the population as the economy is rural economy and agricultural income is insufficient.
- The growth of the economy is also obstructed by social factors like caste system, inheritance and succession, and other outdated traditions.
- The subsidies provided by the government do not reach the needy because of corruption. Corruption stands a great barrier to the eradication of poverty.
EFFECTS OF POVERTY IN INDIA
- Lack of financial stability leads to improper healthcare and high infant mortality rate.
- Child labor emerges as a result of poverty. Poor families don’t tend to enroll their children into school, instead, they send them out to work and earn money to support the family.
- Malnutrition, physical and mental disabilities, diseases related to deficiencies in the diet are also the effects of poverty.
- Illiteracy leads to lack of awareness.
- Unemployment raises levels of crime and in extreme poverty, cases of domestic violence are predominant.
SOLUTIONS ON POVERTY IN INDIA
- India being an agricultural country, the disguised unemployment in agriculture should be removed. Rural economy if strengthened will help in reducing poverty.
- Stability in pricing will make the basic amenities affordable for everyone.
- Skilled labor programs initiated by the government increase the rate of employability.
- Drinking water, sanitation, and education should be made available and awareness regarding the same should be created among people.
- Proper industrialization in regionally poor areas will create greater opportunities and reduce inequality.
- The UN has taken up goals for sustainable development and eradication of poverty and hunger, famously known as the Agenda 2030.
CONCLUSION
India has been tagged as a very consistent ‘developing nation’ and this difference between developing and developed will be achieved only when problems like poverty and hunger will be eradicated. Increase economic growth rate will help in providing infrastructure and facilities also generating employment.
Government schemes can only be implemented successfully when financially stable people stop misusing the ‘Economically Backward Certificate’ and the subsidies actually reach the needy.
Author – Mitali Shingne
Must Explore




India uses measure of absolute poverty to count and eradicate poverty,but instead it should use relative poverty measure so that income inequality gets reduced.And further difference of income between richer and poor class can get stabilised.
Poverty is bip stone in growth of india.India need to start many good programmes to eradicate poverty.Bip reason of poverty is corrupt system.in mnrega basic pay given is 270 per day but it become 150 when reached to rural areas people.